
Courtesy NYC.Gov
Record Flu Cases Hit New York City
By MOHAMED FARGHALY
Mfarghaly@queensledger.com
Millions of Americans are grappling with influenza as the 2025-2026 flu season intensifies across the United States, sending hospitalizations soaring and prompting renewed public health warnings. Health experts say the outbreak, fueled by a particularly severe strain of the virus, may continue for weeks as people return to work, school, and other public spaces following the holiday season.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, at least 41 states are reporting “high” or “very high” flu activity, and visits to doctors for flu-like symptoms have reached levels not seen in nearly three decades. Nationwide, the CDC estimates that influenza has already sickened more than 15 million people, led to roughly 180,000 hospitalizations, and claimed the lives of at least 7,400 individuals, including 17 children. Experts caution that the actual numbers are likely higher, as many cases go unreported.
The 2025-2026 season is outpacing last year’s epidemic, which the CDC had classified as “high severity.” Public health officials are urging vaccinations, especially as some of the most heavily impacted areas, including New York, are experiencing record-setting outbreaks.
“When people refer to a ‘super flu,’ they’re describing how intense and widespread this flu season feels, not a new virus. What we’re seeing in New York is a combination of high community transmission, lower vaccination rates, and winter conditions that allow flu to spread more easily. Together, those factors can lead to more severe illness” said Dr. Maja Castillo, Healthfirst Medical Director.
In New York State, hospitals in the Capital District have reinstated mask requirements for visitors amid the surge, signaling a temporary return to precautions reminiscent of the COVID-19 pandemic. “Masks are making a comeback in 2026,” one official noted, highlighting the seriousness of the current outbreak.
The New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene reported that flu cases this season have already exceeded the peak levels of the previous two seasons. A strain of Influenza A, known as H3 or H3N2, has dominated the state’s cases. Ninety-five percent of reported cases in New York have been Influenza A/H3, while just 5% were Influenza A/H1, according to the department’s latest data. Nationwide, H3N2 has also been the dominant strain, accounting for roughly 86% of Influenza A infections.
Influenza, a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses, can infect the nose, throat, and lungs, leading to mild to severe illness and, in some cases, death, the CDC said. Typical symptoms include cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, body aches, headache, and fatigue.
This season, some doctors have noted unusual gastrointestinal symptoms among patients infected with the H3N2 “super flu.” Reports indicate that many individuals, particularly children, have experienced vomiting of yellow bile, likely caused by suppressed appetite and stomach irritation. Diarrhea has also been observed more frequently in children than adults, raising concerns about dehydration and complications such as bacterial pneumonia.
Data from the New York State Department of Health shows Staten Island alone reported 1,297 flu cases in a single week ending Dec. 27, including 1,035 Influenza A cases, 24 Influenza B cases, and 238 unspecified strains. New York City, unsurprisingly, leads the state in overall cases due to its population density, though statewide totals have reached unprecedented levels this season. Flu activity generally peaks between December and February, suggesting the outbreak may continue for several more weeks.
Medical experts caution that the current H3N2 strain is only moderately covered by this year’s flu vaccine, which was formulated months in advance. Combined with declining vaccination rates nationwide, this leaves more people vulnerable to infection and increases the potential for widespread transmission. The CDC recommends that individuals at high risk—such as older adults, young children, pregnant people, and those with underlying medical conditions—seek antiviral treatment promptly if they develop flu symptoms.
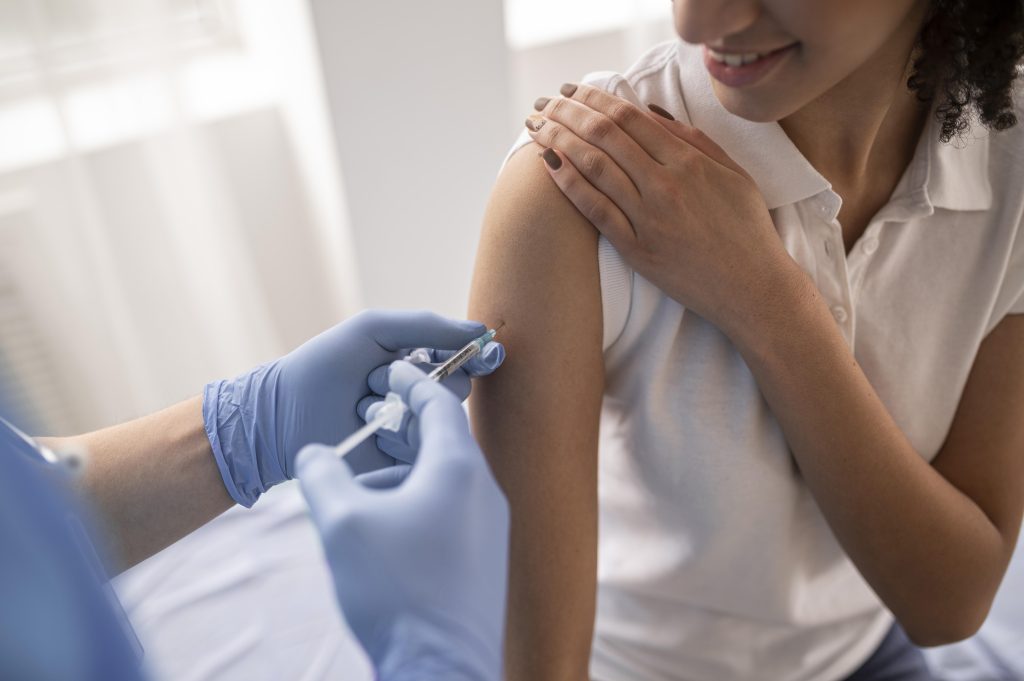
Public health officials are urging all eligible individuals to get vaccinated, practice hand hygiene, and stay home when sick to limit the spread of the virus. While antiviral medications can reduce the severity of illness if administered early, prevention remains the most effective tool.
Courtesy Freepik
“This flu season has already proven to be more severe than many expected, but we still have effective tools. Vaccination, early recognition of symptoms, and antiviral treatment—especially when started within the first 48 hours—can significantly reduce complications and prevent hospitalizations, particularly for children, older adults, and people with chronic conditions,” Castillo said.
As the flu continues to sweep through communities, hospitals are preparing for sustained high patient volumes. The CDC reminds Americans that influenza can affect anyone and encourages vigilance, particularly in crowded settings such as schools, offices, and public transportation.
This flu season serves as a stark reminder that, even after years of navigating COVID-19, seasonal influenza remains a significant public health threat. Experts say that staying current with vaccinations, wearing masks in high-risk settings, and seeking early medical care for flu symptoms are key to mitigating the impact of this year’s outbreak.


