Gutiérrez joins BetaNYC and North Brooklyn Parks Alliance in Mapping Equity Project
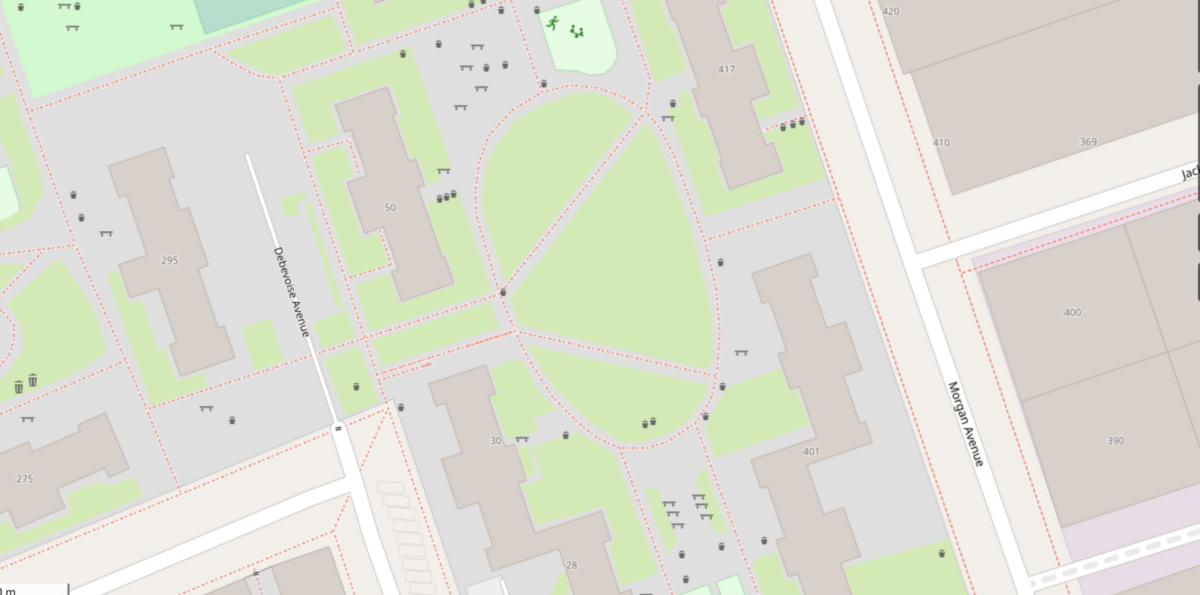
Cooper Park Houses, which a group of attendees learned to map during the event, as mapped on OpenStreetMap.
By Carmo Moniz | news@queensledger.com
A program run by BetaNYC, the North Brooklyn Parks Alliance and councilmember Jennifer Gutiérrez’s office is looking to make data on public resources in the city more equitable across communities, making it easier for communities to advocate for their needs.
The program, called Mapping for Equity, focuses on areas that have been mapped in the least detail. The program uses OpenStreetMap, a mapping software that allows the public to contribute to its features, to map amenities like benches, trash cans, playgrounds and more in public spaces.
BetaNYC, NBPA and Gutiérrez’s office held a launch event for the program last Monday, where they presented the results of their mapping efforts thus far.
Karrie Witkin, a representative for the North Brooklyn Parks Alliance, said that the mapping tool could be useful for the organization as it is focused on the maintenance of public amenities in parks.
“We’re very interested in this tool from a planning perspective and figuring out where we need to be and how to get our services equitably distributed throughout the district,” Witkin said at the event. “This is an exciting tool, it makes visible so much that’s invisible in our maps.”
On OpenStreetMap, wealthier areas are often mapped in greater detail than low-income neighborhoods, which can make using data based arguments for better resources in those neighborhoods difficult, according to the BetaNYC website.
Attendees were able to try mapping for themselves during a field section of the event, and were encouraged to later add their findings to OpenStreetMap. Reverend Dr. Katie Cumiskey, a professor at the College of Staten Island who attended the event, said she hopes to replicate the mapping process on Staten Island.
“It’s really important that citizens of our city feel empowered to be involved in how the city comes to understand the neighborhoods that they live in, especially for those folks who live in public housing or neighborhoods that have been historically excluded or underserved by the city,” Cumiskey said in an interview. “BetaNYC has a really fun and cool way for folks to feel like they can engage with how the city interprets and views their neighborhoods.”
BetaNYC has had two cohorts of Civic Innovation Fellows, all City University of New York students who were matched with the fellowship through a university program, participate in the Mapping for Equity program. Together, the two cohorts mapped over 5,100 features in OpenStreetMap, according to BetaNYC fellowship manager Jazzy Smith.
Kinji Donald, one of the fellows who worked on the project, said that once features are uploaded to OpenStreetMap, they take around a week to be visible to the public.
“I feel like I’m actually making a change and helping the public,” Donald said in an interview. “Hopefully we can see certain patterns that will allow us to see areas that may need more amenities, or may have a lot of damaged amenities that need fixing, and we can take care of.”
Noel Hidalgo, BetaNYC’s executive director and a Technology & Democracy fellow at Harvard University’s Ash Center for Democratic Governance and Innovation, said he hopes to work with nonprofit organizations and other community groups to use the mapping data for advocacy purposes.
“The fight for open data is about getting the opportunity for everyone, not just government, take the information and use it for analytical purposes,” Hidalgo said in the interview. “Something that we’re very, very passionate about is figuring out how communities and individuals can take that information and use it for their local advocacy purposes.”
Anya Lehr, Gutiérrez’s senior adviser, said that as chair of the New York City Council’s Technology Committee, the councilmember has seen the inequalities caused by technological infrastructure, and that it can be difficult to make arguments for addressing issues in a community without quantitative data to back them.
“When she started thinking about all the other inequalities, which there are a lot from a long time of not having investments, the thing that we would always do is go ‘well where’s the data?’” Lehr said at the event. “Super excited to be working on this project with everyone, as soon as we saw this, as soon as Jazzy showed us what came out of this, it was like ‘this is awesome.’”
Hidalgo said BetaNYC began working with Councilmember Gutiérrez around a year ago, and that she had continued the work of her predecessor, now Brooklyn Borough President Antonio Reynoso, in providing funding for the organization’s data literacy work.
BetaNYC has been running literacy classes for OpenData, a government platform that includes public datasets ranging from crime statistics to film permit data, since former Mayor Michael Bloomberg passed the “Open Data Law” in 2012. The law required that by the end of 2018, all public datasets be accessible on a single portal online.
Hidalgo said that the organization uses mapping to teach how to use OpenData, an idea that arose when gathering in office spaces for literacy programs became difficult due to the pandemic. He also said that the next step in the project is working with BetaNYC’s community partners, such as NBPA, and teaching them to run data collecting events, data entry and how to maintain the data.
“This project is just one rung in the ladder of a very long ladder of data literacy,” Hidalgo said in the interview. “We now have a nuts-to-soup perspective of how to teach and how to collect data, and walk you as the general public into the context of collecting data.”